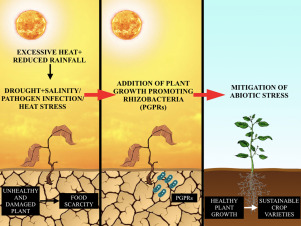
There are several potential causes for plant growth to decrease. Among the most common are insufficient light, excessive heat or cold, nutrient deficiencies, water stress, and pests or diseases. Any of these can cause stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and other signs of distress.
In some cases, addressing the underlying problem can help improve plant health and encourage new growth.
One of the most common reasons that plants experience decreased growth is because they are not receiving enough light. If a plant is not getting enough sunlight, it will begin to stretch out and become leggy in an attempt to reach the light. This stretching causes the plant to produce fewer leaves, which results in less photosynthesis and ultimately slower growth.
Another reason for decreased plant growth is insufficient nutrients. Plants need a variety of minerals and nutrients from the soil in order to thrive. If they are not getting these essential elements, they will slowly start to decline.
A lack of nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium can all lead to stunted growth and yellowing leaves.
Finally, too much or too little water can also cause problems for plants. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering will cause the leaves to wilt and the plant to stop growing altogether.
It’s important to find a happy medium when watering your plants – giving them just enough so that they stay healthy and continue growing at a steady pace.
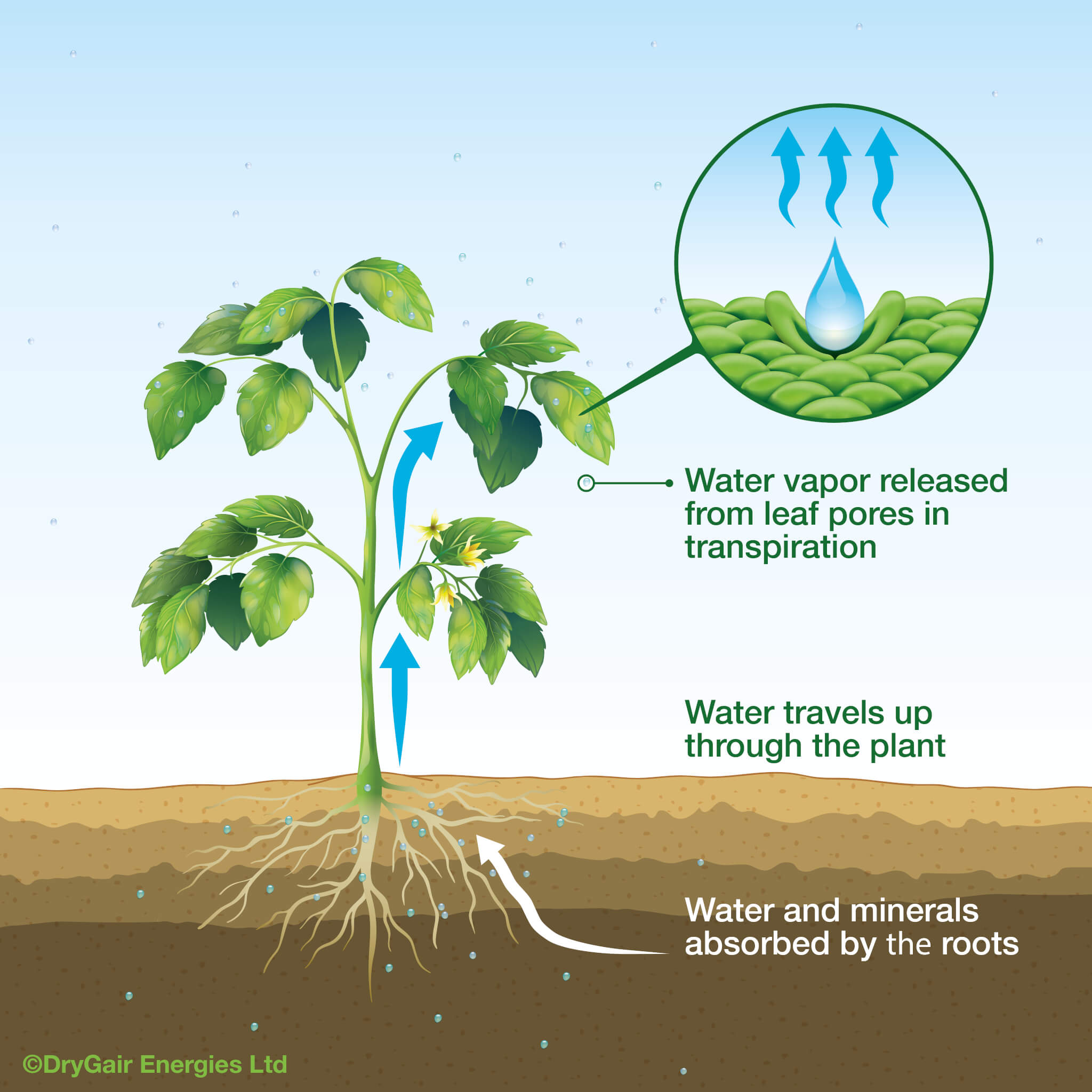
Credit: drygair.com
What Can Decrease Plant Growth?
There are a number of reasons why plant growth may be stunted or decreased. One common reason is due to insufficient light. If a plant isn’t getting enough sunlight, it will likely grow slowly or not at all.
Another reason for decreased plant growth can be due to poor soil conditions. Plants need nutrient-rich soil in order to thrive, so if the soil is lacking in nutrients, plants will likely suffer as a result. Finally, extreme temperatures can also impede plant growth; both too hot and too cold temperatures can damage plants and cause them to grow more slowly or stop growing altogether.
What Causes Plant Growth to Increase Decrease?
There are many different factors that can affect plant growth, and how those factors interact with each other can cause either an increase or decrease in growth. Some of the most important factors include light, temperature, water, nutrients, and carbon dioxide levels.
Light is one of the most important factors for plant growth.
Plants need light for photosynthesis, which is how they convert sunlight into energy that they can use to grow and thrive. Too little light will result in stunted growth, while too much light can actually damage plants. The ideal amount of light will depend on the specific plant species.
Temperature is another critical factor for plant growth. Most plants prefer a relatively warm climate, though some can tolerate colder temperatures. Extreme heat or cold can injure or kill plants.
Again, the ideal temperature range will vary depending on the species of plant.
Water is vital for all plant life, as it helps to transport nutrients and minerals throughout the plant tissue. Without enough water, plants will wilt and eventually die.
However, too much water can also be detrimental as it can lead to root rot and other problems. The key is to maintain a consistent level of moisture in the soil without letting it get too wet or too dry.
Nutrients are essential for healthy plant growth as they provide the building blocks needed for cell development and metabolism.
A lack of nutrients will result in stunted growth and yellowing leaves, while an excess of certain nutrients (such as nitrogen) can actually be toxic to plants. It’s important to have a good balance of all essential nutrients in order to promote optimal plant health.
What are the 6 Factors Affecting Plant Growth?
There are six primary factors that affect plant growth: light, temperature, water, nutrients, carbon dioxide and oxygen. Each of these factors can influence plant growth in both positive and negative ways.
Light is one of the most important factors affecting plant growth.
Plants need light for photosynthesis, the process by which they convert sunlight into energy. Too little light will result in slow or stunted growth, while too much light can damage leaves and cause scorching. The intensity, duration and quality of light all play a role in optimal plant growth.
Temperature also plays a vital role in plant growth. Most plants prefer average temperatures between 68-77 degrees Fahrenheit (20-25 degrees Celsius). However, different plants have different ideal temperature ranges.
For example, tropical plants generally require higher temperatures than temperate plants. Extremely high or low temperatures can damage plants and inhibit growth.
Water is another essential factor for plant growth.
Plants need water for photosynthesis as well as to transport nutrients throughout their system. Too little water will result in wilting and eventual death, while too much water can cause root rot. The frequency and amount of watering required varies depending on the type of plant; some species need to be watered daily while others only require weekly watering.
Nutrients are essential for all aspects of plant growth including photosynthesis, cell division and metabolic processes. There are many different types of nutrients needed by plants including nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium among others. These nutrients are typically found in soil but may also need to be added through fertilizers depending on the level of depletion in the soil.
. Nutrient deficiencies can lead to poor plant health and stunted growth while an overabundance of certain nutrients can actually be toxic to plants..
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is another important factor influencing photosynthesis and thereforeplantgrowth.. Although CO2 levels in air naturally fluctuate,, humans have significantly increased atmospheric CO2 levels through activities such as burning fossil fuelsand deforestation., This increase has been linked with enhanced vegetative growthevenin drought conditions., However,, it’s important to note that too much CO2can actuallybe harmfulto someplant species .
Oxygenis also necessary for proper plant function though it is not often thought about when discussing factors affectingplantgrowth., Oxygen helps with respiration,, a process whereby plants produce ATP (energy) from glucose molecule s.
What are 3 Limiting Factors That Affect Plant Growth?
There are three primary limiting factors that affect plant growth: water, light, and nutrients.
Water is essential for plant growth as it is used for photosynthesis, transport of nutrients, and cell turgor. However, too much or too little water can both limit plant growth.
For example, drought stress can reduce photosynthesis and lead to wilting due to lack of cell turgor. Conversely, flooding can also cause problems by leading to anaerobic conditions which can prevent nutrient uptake and promote root rot.
Light is another important factor for plants as it is used for photosynthesis.
However, too much light can be damaging as it can lead to photoinhibition. Additionally, shade from other plants or objects can limit the amount of light available to a particular plant resulting in reduced growth.
Finally, nutrients are necessary for plant growth as they are used in various metabolic processes.
However, if soils are lacking in certain nutrients or if roots cannot access them due to poor aeration then growth will be limited.
Leaf Curling Disease in Chili Pepper, Capsicum & Tomato Plants | How to Identify, Prevent & Cure it?
What is the Most Important Factor for Plant Growth
One of the most important factors for plant growth is sunlight. Sunlight helps plants to photosynthesize, which produces the energy they need to grow. Plants also need water and nutrients from the soil to survive and thrive.
If any of these elements are lacking, it can stunt a plant’s growth or even kill it.
What are the 5 Factors Affecting Plant Growth
There are a number of factors that can affect plant growth. These include light, temperature, water, nutrients, and pests. Let’s take a closer look at each one.
Light is one of the most important factors for plant growth. Plants need light for photosynthesis, which is how they make their food. The amount of light that a plant gets can affect its growth rate and how much it produces.
Temperature is another important factor affecting plant growth. Different plants prefer different temperature ranges. If the temperature is too cold or too hot, it can stress the plants and slow down their growth.
Water is also essential for plant growth. Too little water will cause the plants to wilt and eventually die. Too much water can also be harmful as it can drown the roots and promote fungal growth.
Nutrients are another vital element for plant growth. Plants need a range of different minerals and vitamins to grow properly. These nutrients can come from the soil or from fertilizer applied to the plants’ leaves or roots.
Pests can also have a big impact on plant growth.
What are the Factors That Affect the Growth of Plants
The growth of plants is affected by a number of factors, including light, water, temperature, nutrients, and soil type. Let’s take a closer look at each of these factors and how they can impact plant growth.
Light is one of the most important factors for plant growth.
Plants need light for photosynthesis, which is how they convert sunlight into energy to fuel their growth. The amount of light that a plant gets can affect its growth rate, as well as the shape and size of the plant. Too little light will result in stunted growth, while too much light can damage leaves or cause them to wilt.
Water is another essential factor for plant growth. Plants need water for hydration and to transport nutrients throughout their system. The amount of water a plant gets can impact its growth rate and health.
Too little water will cause the plant to wilt and eventually die, while too much water can lead to root rot or other problems.
Temperature is also important for plant growth. Most plants prefer moderate temperatures and will not thrive in extreme conditions.
Too much heat can damage leaves or cause them to dry out, while too cold temperatures can inhibit photosynthesis or even kill the plant outright. It’s important to find the right balance when it comes to temperature if you want your plants to flourish.
Nutrients are another key factor inplantgrowth .
Plants need nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus ,and potassium for healthy growth . These nutrients are typically found in the soil , but they can also be added through fertilizers . If plants don’t get enough nutrients , they may become yellow or sickly looking .
On the other hand , too many nutrients can actually be harmful to plants . It’s important to strike a balance when it comes to feeding your plants .
Growing Vegetables, Flowers, Fruits And Decorative Plants for Commercial Purpose is Known As___
Growing vegetables, flowers, fruits and decorative plants for commercial purpose is known as horticulture. Horticulturists grow a wide variety of plants in controlled or natural environments, using knowledge of plant science and technology. They work in greenhouses, nurseries, gardens and parks.
Some horticulturists also work in the food processing and floral industries.
Environmental Factors Affecting Plant Growth Pdf
Environmental factors are those that affect the growth and development of plants. These can be both biotic and abiotic. The main environmental factors affecting plant growth pdf are light, water, temperature, humidity, and soil type.
Light is one of the most important environmental factors for plant growth pdf. It affects photosynthesis, which is necessary for the plant to create its own food. too little light will result in stunted growth, while too much light can damage leaves.
The amount of light also affects the color of flowers and other parts of the plant.
Water is another important factor affecting plant growth pdf. Plants need water for photosynthesis as well as to transport nutrients throughout their bodies.
Too little water will cause wilting and eventually death, while too much water can drown a plant. The quality of water can also affect plants; pollutants such as heavy metals can damage roots and leaves.
Temperature is another key factor influencing plant growth pdfs; most plants prefer a moderate temperature range between 60-80 degrees Fahrenheit (15-27 degrees Celsius).
Extreme temperatures outside of this range can damage or kill plants. Temperature also affects how quickly a plant grows; warmer temperatures typically lead to faster growth rates than cooler ones.
Soil type is yet another factor that plays a role in how well plants grow pdfs .
Different types of soils contain different amounts of essential nutrients needed by plants; sandier soils tend to have fewer nutrients than more clayey soils . Soil pH levels (acidity/alkalinity) can also affect how well plants grow; most prefer slightly acidic conditions with a pH between 6 and 7 . Too much or too little acidity/alkalinity can limit nutrient availability and stunt growth .
Environmental Factors Affecting Plant Growth
There are many environmental factors that can affect plant growth. Some of these factors include light, temperature, water, and soil.
Light is one of the most important environmental factors for plant growth.
Plants need light for photosynthesis, which is how they make food. The amount of light that a plant gets can affect its growth rate, shape, and size. Too much or too little light can be harmful to plants.
Temperature is another important factor for plant growth. Different plants have different ideal temperatures for growth. Most plants do best in warm temperatures, but some plants prefer cooler temperatures.
Extremely hot or cold temperatures can damage plants.
Water is essential for plant growth. Plants use water for photosynthesis and to transport nutrients throughout their bodies.
Too much or too little water can harm plants. Soil moisture content also affects plant growth; if the soil is too dry, it will limit the amount of water available to the roots and may stunt the plant’s growth.
The type of soil a plant grows in can also affect its growth.
Soil Factors Affecting Plant Growth
There are many factors that can affect plant growth, but one of the most important is soil. The type of soil, its nutrient content, pH level, and drainage all play a role in how well plants will grow.
One of the first things to consider when choosing a location for your garden is the type of soil present.
Sandy soils are well-aerated and drain quickly, while clay soils are dense and hold moisture well. Loamy soils are a mix of the two and tend to be the best for growing plants.
The nutrient content of the soil is also important for plant growth.
Soils with low levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium will result in stunted growth or yellowing leaves. To ensure that your plants have enough nutrients, you can either amend the soil with fertilizer or choose plants that are known to be tolerant of poor soils.
The pH level of the soil can also affect plant growth.
Most plants prefer slightly acidic soils with a pH between 6 and 7. If the soil is too alkaline or too acidic, it can lead to nutrient deficiencies or poor root development. You can test your soil’s pH level with a simple kit from your local gardening store.
Finally, good drainage is essential for healthy plant growth.
What Prevents Plants from Growing
One of the most common problems that gardeners face is that their plants just won’t grow. There are a number of possible reasons for this, but thankfully, there are also solutions. In this blog post, we’ll explore some of the most common reasons why plants don’t grow, and what you can do to fix the problem.
One of the most common reasons for stunted plant growth is simply that the plant isn’t getting enough light. This is especially common in indoor gardens, where natural light may be limited. If your plants are not getting enough light, they will likely become spindly and weak, and they may even stop growing altogether.
The solution to this problem is simple: move your plants to a location where they will receive more light. If you’re growing indoors, consider using grow lights to give your plants the light they need to thrive.
Another common reason for poor plant growth is incorrect watering.
Overwatering can drown roots and prevent them from absorbing nutrients, while underwatering can cause leaves to wilt and drop off. To ensure proper watering, check the soil before watering; if it’s already moist, there’s no need to water again until it begins to dry out. It’s also important to choose a potting mix that drains well; otherwise, your plant may never get the chance to dry out between waterings.
Finally, nutrient deficiencies can also cause problems with plant growth. Plants need a variety of nutrients to thrive, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. If any of these nutrients are lacking in the soil, it can lead to stunted growth or yellowing leaves (a condition known as chlorosis).
Conclusion
There are several reasons why plant growth may decrease. One reason is that the plant isn’t getting enough light. If a plant isn’t getting enough light, it won’t be able to photosynthesize and make food for itself, which will lead to stunted growth.
Another reason for decreased growth could be lack of water. Plants need water to transport nutrients and minerals throughout their system, and without enough water, they can’t function properly. Lastly, poor soil quality can also lead to decreased growth in plants.
If the soil doesn’t have enough nutrients or if it’s too compacted, plants won’t be able to grow as well.