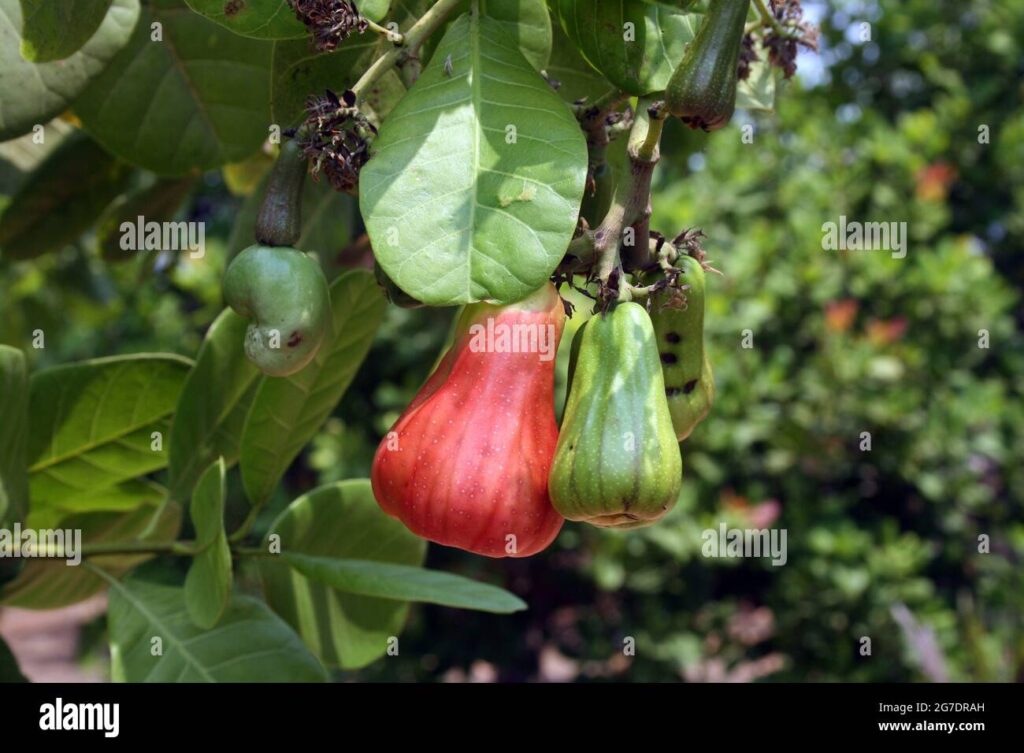
The cashew tree is native to northeastern Brazil. Cashews are widely grown in tropical countries around the world, including India, Vietnam, and Nigeria. The cashew fruit grows on a large evergreen tree that can reach up to 30 meters in height.
The tree has a dense canopy of leaves and produces small white flowers. The fruit of the cashew tree is an oval-shaped drupe that hangs from the end of the branch. The outer shell of the fruit contains a poisonous oil called urushiol.
The inner flesh of the fruit is sweet and edible, and it surrounds a single seed known as the cashew nut.
Cashew fruits come in many different shapes, sizes, and colors. They can be small and round or long and slender. The color of the fruit can range from green to yellow to red.
The flesh of the fruit is sweet and juicy. The seed, or nut, of the cashew fruit is encased in a hard shell.
Cashews are native to Brazil, but they are now grown in many tropical countries.
In addition to being eaten fresh, cashews are also used in cooking. They can be roasted and salted, or ground into a powder that is used as a flavoring agent in many dishes.
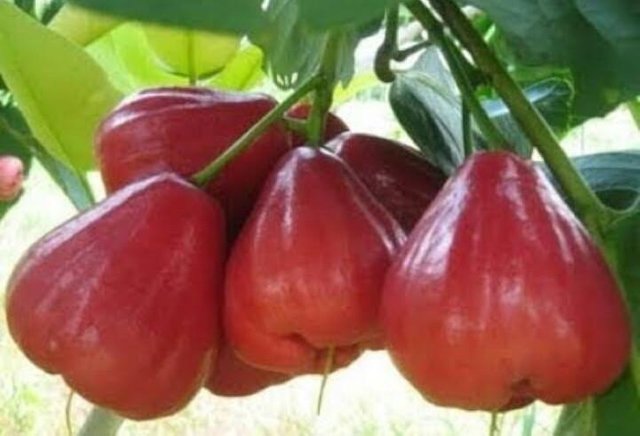

Credit: steemit.com
What are the Types of Cashew?
There are two types of cashew: the sweet cashew and the sour cashew. The sweet cashew is the most popular type of cashew. It has a mild, sweet flavor and is often used in desserts.
The sour cashew is less popular and has a tart, acidic flavor. It is often used in savory dishes or as a garnish.
How Many Types of Cashew Do We Have?
There are actually two types of cashews – the sweet cashew and the bitter cashew. The sweet cashew is the type that we usually eat, while the bitter cashew is used more for its oil.
Which Variety of Cashew is Best?
The cashew is a popular tree nut that is often used in various cuisines. There are many different varieties of cashews, but which one is the best?
In general, there are two main types of cashews: the sweet variety and the bitter variety.
The sweet variety is often used in desserts or as a snack, while the bitter variety is typically used in savory dishes.
So, which type of cashew is best? It really depends on your personal preference.
If you prefer a sweeter taste, then the sweet variety may be better for you. If you prefer a more savory flavor, then the bitter variety may be a better option. Ultimately, it all comes down to what you like!
What is Difference between W400 And W320 Cashew?
The W320 and W400 grades of cashew refer to the size of the kernel. The W320 grade has kernels that are smaller in size, while the W400 grade has kernels that are larger in size. The difference in size is due to the different growing conditions of the trees that produce these nuts.
The W320 cashews are grown in areas with higher rainfall, while the W400 cashews are grown in areas with lower rainfall. This results in a difference in yield, with more nuts being produced from a single tree when grown under higher rainfall conditions. Cashews that are harvested from trees grown under higher rainfall conditions will have a higher moisture content and be softer than those harvested from trees grown under lower rainfall conditions.
Cashew varieties
Cashew Fruit Edible
Cashew Fruit Edible
The cashew fruit is the edible part of the cashew tree, which is native to Brazil. The fruit is also known as Cashew Apple or Caju in Portuguese.
It has a sweet, slightly acidic taste and is often used in jams and juices.
The cashew apple is rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, potassium and magnesium. It also contains antioxidants that may help protect against some chronic diseases.
Cashew Fruit Taste
Cashew fruits are a type of drupe, or stone fruit. They grow on trees and have a sweet, nutty taste. The cashew tree is native to Brazil, but the fruit is now grown in many tropical countries.
The cashew fruit has a thick outer shell that contains a poisonous oil. This oil can cause skin irritation, so the fruit must be handled with care. The inner flesh of the fruit is edible and has a sweet, nutty flavor.
Cashew fruits are often used in desserts and snacks.
The cashew tree grows best in warm, humid climates. It can reach up to 40 feet (12 meters) tall and produces small yellowish-green flowers.
The tree produces two types of fruit: the cashew apple and the cashew nut.
The cashew apple is the fleshy part of the fruit that surrounds the seed, or nut. It is red or yellow when ripe and has a sweet flavor similar to pineapple or mango.
The apple is not as popular as the nut, but it can be used to make juices and jams.
The cashew nut is encased in a hard shell that contains an oily substance called urushiol . This substance can cause skin irritation, so nuts should be roasted before they are eaten .
Roasting also enhances their flavor .Cashews are a popular snack food , often eaten roasted and salted .
Cashew Nut
Cashew nuts are the seeds of the cashew tree, which is native to Brazil. Thetree grows to a height of 20-30 feet and produces a fruit called the cashewapple. The apple is edible, but the nut is the part that is most oftenconsumed.
Cashews are relatively low in calories compared to other nuts, with about 155 calories per ounce. They are also a good source of dietary fiber and protein. In addition, cashews contain several essential nutrients including magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, and copper.
Cashews can be eaten whole, roasted, or as part of various dishes such as curries or stir-fries. They can also be used in desserts or made into a paste for use in sauces or spreads.
Cashew Tree
The cashew tree is a tropical evergreen that produces the cashew nut. The tree can grow as high as 14 m (46 ft), but the dwarf cashew, growing up to 6 m (20 ft), has proved more profitable, with earlier maturity and higher yields. The cashew nut, often called a cashew, is widely consumed.
It is eaten on its own, used in recipes, or processed into cashew cheese or cashew butter.
The leaves of the cashew tree are simple and spirally arranged; they are 20–35 cm (8–14 in) long and 15–25 cm (6–10 in) wide. The flowers are produced in a panicle 30–50 cm (12–20 in) long; each flower is small, pale green at first then turning red, with five petals 7–12 mm (0.3–0.5 in) long.
The largest fruit-bearing tree in the world, the African oil palm Elaeis guineensis,[2] reaches 30 m (100 ft) tall and bears 5 kg (11 lb) of fruit bunches weighing 31 kg (68 lb)[3] each year.[4][5] An average-sized oil palm tree may yield 200 fruits yearly,[6][7] even more when grown under optimum conditions.[8][9] Cashews belong to the same family as pistachios and mangoes; all three trees produce drupes: fleshy fruit with thin skin and single stone or pit.
[10][11][12]
Cashews are native to northeastern Brazil.[13][14] Portuguese colonists brought them to India and Africa after discovering them while seeking slaves for their Brazilian sugar plantations around 1560.[15]:65 Commercial production of cashews began only after Indian independence from Portugal in 1947[16]:89 although large scale planting did not begin until 1963 because of lack of availability of plant stock caused by natural disasters such as hurricanes which destroyed crops.
[17]:113 India continues to be by far the largest producer followed by Vietnam,[18]:114 Ivory Coast,[19]:115 Tanzania[20](page needed):116 Nigeria[21](page needed):117 Guinea Bissau[22](page needed):118 Mozambique:[23]
Cashew Fruit Benefits
Cashew fruits are not only delicious but also offer a range of health benefits. Here are some of the top cashew fruit benefits:
1. Cashews are a good source of antioxidants.
2. Cashews can help improve blood circulation.
3. Cashews can help lower cholesterol levels.
4. Cashews can aid in weight loss.
5. Cashews can help strengthen bones and teeth.
Cashew Plant
The cashew plant is a tropical evergreen tree that produces the cashew nut. It can grow as high as 14 m (46 ft) but the dwarf cashew, growing up to 6 m (20 ft), has proved more profitable, with earlier maturity and higher yields. The leaves are arranged in pairs or whorls of three or four, each leaf has two small stipules at its base.
The flowers are produced singly or in short panicles arising from axillary buds; they are white or pale pink, and have five petals and numerous stamens.
The fruit of the cashew tree is an accessory fruit (sometimes called a pseudocarp or false fruit). What appears to be the fruit is an oval or pear-shaped “false fruit” or peduncle 4–5 cm (1.6–2.0 in) long and 3 cm (1.2 in) broad at the base near where it attaches to the stem of the true fruit.[10]
This pseudocarp develops first on the tree, becoming green and enlarged as it grows; when mature it turns reddish-brown and papery, eventually disintegrating to reveal the shiny red-brown nut inside.
Cashew Scientific Name And Family
The cashew tree is a tropical evergreen that produces the cashew nut. The tree can grow as high as 20 m (66 ft), but the dwarf cultivars, growing up to 12 m (39 ft), are more commonly cultivated. Cashews are native to northeastern Brazil.
Commercial production of cashews began in colonial Brazil, and eventually spread to India and Africa. Portuguese colonists in Brazil began exporting cashews from Brazil during the mid-16th century.[1] India remains today the largest producer of cashews, followed by Vietnam and Nigeria.
The scientific name for the Cashew tree is Anacardium Occidentale. It is also known as Cardus Indicus or Jambu Pala in Indonesia. The family it belongs to is the Anacardiaceae which also includes mango, pistachio and poison ivy!
The fruit of the Cashew tree is actually not a nut at all, but rather a drupe. A drupe is defined as a fleshy fruit with a stony seed surrounded by an outer hull or husk; think peaches, plums or cherries. The “nut” we eat is actually this seed that sits below the fleshycashew apple (which itself isn’t eaten because it contains urushiol, which causes contact dermatitis).
Conclusion
Cashew fruits come in two different types: the cashew apple and the cashew nut. The cashew apple is the fruit of the cashew tree, while the cashew nut is actually a seed that grows inside of the fruit. Both the fruit and the nut are edible, but they have different flavor profiles.
The cashew apple is sweet and tangy, while the cashew nut is rich and buttery.